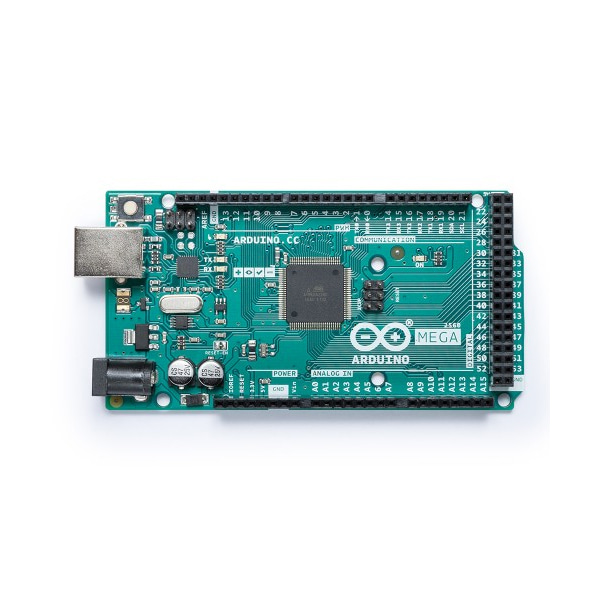
정품 아두이노 메가 2560 R3
(ARDUINO MEGA 2560 REV3)
개요
- 정품 아두이노 메가2560 보드입니다.
- 두이노 메가 2560은 ATmega2560(datasheet) 기반의 마이크로컨트롤러 보드로 54개의 디지털 입출력 핀(그중 15개는 PWM 출력), 16개의 아날로그 입력, 4개의 UART(하드웨어 시리얼 포트), 16Mhz 크리스탈 오실레이터, USB, 파워잭, ICSP헤더, 리셋버튼을 포함하고 있습니다. 아두이노 메가는 아두이노 Due 혹은 Diecimila용으로 디자인된 대부분의 쉴드와 호환됩니다.
- 아두이노 메가 2560은 아두이노 메가(Arduino Mega)의 업데이트 버전입니다.
- 아두이노 메가2560은 FTDI USB-to-Serial 드라이버칩을 사용 하지 않는 다는 점에서 이전버전의 보드들과 다르며, 대신 USB-to_serial 컨버터로 프로그래밍된 Atmega16U2 칩을 장착하고 있습니다.
- 아두이노 메가 Revision 2는 8U2 HWB라인을 그라운드로 만들어주는 저항을 가지고 있어 쉽게 DFU mode 에 들어가게 합니다.
- 아두이노 메가 revision 3는 아래와 같은 새로운 기능을 가지고 있습니다:
- 1.0 pinout: AREF 핀 근처에 SDA, SCL 핀을 추가. RESET핀 옆에 새로운 두개의 핀을 추가. 하나는 IOREF핀으로 아두이노 보드가 사용하는 전압을 확인할 수 있게 하여주며, 나머지 하나는 미래의 사용을 위해 예약되어 있습니다.
- 좀더 강해진 RESET 회로
- Atmega16U2는 이전버전의 8U2 칩을 대치
특징
-
Microcontroller ATmega2560 Operating Voltage 5V Input Voltage (recommended) 7-12V Input Voltage (limit) 6-20V Digital I/O Pins 54 (of which 15 provide PWM output) Analog Input Pins 16 DC Current per I/O Pin 20 mA DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50 mA Flash Memory 256 KB of which 8 KB used by bootloader SRAM 8 KB EEPROM 4 KB Clock Speed 16 MHz LED_BUILTIN 13 Length 101.52 mm Width 53.3 mm Weight 37 g
문서
-
OSH: Schematics
Arduino Mega 2560 is open-source hardware! You can build your own board using the follwing files:
EAGLE FILES IN .ZIPSCHEMATICS IN . PDFBOARD SIZE IN .DXF
Programming
The Mega 2560 board can be programmed with the Arduino Software (IDE). For details, see thereference and tutorials.
The ATmega2560 on the Mega 2560 comes preprogrammed with a bootloader that allows you to upload new code to it without the use of an external hardware programmer. It communicates using the original STK500 protocol (reference, C header files).
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the microcontroller through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header using Arduino ISP or similar; see these instructions for details.
The ATmega16U2 (or 8U2 in the rev1 and rev2 boards) firmware source code is available in theArduino repository. The ATmega16U2/8U2 is loaded with a DFU bootloader, which can be activated by:
- On Rev1 boards: connecting the solder jumper on the back of the board (near the map of Italy) and then resetting the 8U2.
- On Rev2 or later boards: there is a resistor that pulling the 8U2/16U2 HWB line to ground, making it easier to put into DFU mode. You can then use Atmel's FLIP software (Windows) or the DFU programmer (Mac OS X and Linux) to load a new firmware. Or you can use the ISP header with an external programmer (overwriting the DFU bootloader). See this user-contributed tutorial for more information.
Warnings
The Mega 2560 has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. Although most computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an extra layer of protection. If more than 500 mA is applied to the USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is removed.
Power
The Mega 2560 can be powered via the USB connection or with an external power supply. The power source is selected automatically.
External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the GND and Vin pin headers of the POWER connector.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply less than five volts and the board may become unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board. The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The power pins are as follows:
- Vin. The input voltage to the board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the USB connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin.
- 5V. This pin outputs a regulated 5V from the regulator on the board. The board can be supplied with power either from the DC power jack (7 - 12V), the USB connector (5V), or the VIN pin of the board (7-12V). Supplying voltage via the 5V or 3.3V pins bypasses the regulator, and can damage your board. We don't advise it.
- 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board regulator. Maximum current draw is 50 mA.
- GND. Ground pins.
- IOREF. This pin on the board provides the voltage reference with which the microcontroller operates. A properly configured shield can read the IOREF pin voltage and select the appropriate power source or enable voltage translators on the outputs for working with the 5V or 3.3V.
Memory
The ATmega2560 has 256 KB of flash memory for storing code (of which 8 KB is used for the bootloader), 8 KB of SRAM and 4 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library).
Input and Output
See the mapping between Arduino pins and Atmega2560 ports:
Each of the 54 digital pins on the Mega can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(),digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive 20 mA as recommended operating condition and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 k ohm. A maximum of 40mA is the value that must not be exceeded to avoid permanent damage to the microcontroller.
In addition, some pins have specialized functions:
- Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX); Serial 1: 19 (RX) and 18 (TX); Serial 2: 17 (RX) and 16 (TX); Serial 3: 15 (RX) and 14 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. Pins 0 and 1 are also connected to the corresponding pins of the ATmega16U2 USB-to-TTL Serial chip.
- External Interrupts: 2 (interrupt 0), 3 (interrupt 1), 18 (interrupt 5), 19 (interrupt 4), 20 (interrupt 3), and 21 (interrupt 2). These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low level, a rising or falling edge, or a change in level. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
- PWM: 2 to 13 and 44 to 46. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
- SPI: 50 (MISO), 51 (MOSI), 52 (SCK), 53 (SS). These pins support SPI communication using theSPI library. The SPI pins are also broken out on the ICSP header, which is physically compatible with the Arduino /Genuino Uno and the old Duemilanove and Diecimila Arduino boards.
- LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off.
- TWI: 20 (SDA) and 21 (SCL). Support TWI communication using the Wire library. Note that these pins are not in the same location as the TWI pins on the old Duemilanove or Diecimila Arduino boards.
See also the mapping Arduino Mega 2560 PIN diagram.
The Mega 2560 has 16 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and analogReference() function.
There are a couple of other pins on the board:- AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
- Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board.
Communication
The Mega 2560 board has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another board, or other microcontrollers. The ATmega2560 provides four hardware UARTs for TTL (5V) serial communication. An ATmega16U2 (ATmega 8U2 on the revision 1 and revision 2 boards) on the board channels one of these over USB and provides a virtual com port to software on the computer (Windows machines will need a .inf file, but OSX and Linux machines will recognize the board as a COM port automatically. The Arduino Software (IDE) includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the board. The RX and TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the ATmega8U2/ATmega16U2 chip and USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Mega 2560's digital pins.
The Mega 2560 also supports TWI and SPI communication. The Arduino Software (IDE) includes a Wire library to simplify use of the TWI bus; see the documentation for details. For SPI communication, use the SPI library.
Physical Characteristics and Shield Compatibility
The maximum length and width of the Mega 2560 PCB are 4 and 2.1 inches respectively, with the USB connector and power jack extending beyond the former dimension. Three screw holes allow the board to be attached to a surface or case. Note that the distance between digital pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"), not an even multiple of the 100 mil spacing of the other pins.
The Mega 2560 is designed to be compatible with most shields designed for the Uno and the older Diecimila or Duemilanove Arduino boards. Digital pins 0 to 13 (and the adjacent AREF and GND pins), analog inputs 0 to 5, the power header, and ICSP header are all in equivalent locations. Furthermore, the main UART (serial port) is located on the same pins (0 and 1), as are external interrupts 0 and 1 (pins 2 and 3 respectively). SPI is available through the ICSP header on both the Mega 2560 and Duemilanove / Diecimila boards. Please note that I2C is not located on the same pins on the Mega 2560 board (20 and 21) as the Duemilanove / Diecimila boards (analog inputs 4 and 5).
Automatic (Software) Reset
Rather then requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Mega 2560 is designed in a way that allows it to be reset by software running on a connected computer. One of the hardware flow control lines (DTR) of the ATmega8U2 is connected to the reset line of the ATmega2560 via a 100 nanofarad capacitor. When this line is asserted (taken low), the reset line drops long enough to reset the chip. The Arduino Software (IDE) uses this capability to allow you to upload code by simply pressing the upload button in the Arduino environment. This means that the bootloader can have a shorter timeout, as the lowering of DTR can be well-coordinated with the start of the upload.
This setup has other implications. When the Mega 2560 board is connected to either a computer running Mac OS X or Linux, it resets each time a connection is made to it from software (via USB). For the following half-second or so, the bootloader is running on the ATMega2560. While it is programmed to ignore malformed data (i.e. anything besides an upload of new code), it will intercept the first few bytes of data sent to the board after a connection is opened. If a sketch running on the board receives one-time configuration or other data when it first starts, make sure that the software with which it communicates waits a second after opening the connection and before sending this data.
The Mega 2560 board contains a trace that can be cut to disable the auto-reset. The pads on either side of the trace can be soldered together to re-enable it. It's labeled "RESET-EN". You may also be able to disable the auto-reset by connecting a 110 ohm resistor from 5V to the reset line; see this forum thread for details.
Revisions
The Mega 2560 does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip used in past designs. Instead, it features the ATmega16U2 (ATmega8U2 in the revision 1 and revision 2 Arduino boards) programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
Revision 2 of the Mega 2560 board has a resistor pulling the 8U2 HWB line to ground, making it easier to put into DFU mode.
Revision 3 of the Arduino board and the current Genuino Mega 2560 have the following improved features:- 1.0 pinout: SDA and SCL pins - near to the AREF pin - and two other new pins placed near to the RESET pin, the IOREF that allow the shields to adapt to the voltage provided from the board. In future, shields will be compatible both with the board that use the AVR, which operate with 5V and with the board that uses ATSAM3X8E, that operate with 3.3V. The second one is a not connected pin, that is reserved for future purposes.
- Stronger RESET circuit.
- Atmega 16U2 replace the 8U2.